Orbital Debris Mitigation & Remediation
Topic outline
-
Orbital debris is a growing concern due to the continuous and rapid accumulation of objects in space, including expended satellites, satellite or launch vehicle components, and fragments resulting from the collision between space objects. The number of significant satellite breakup events has averaged about four per year and the cataloged debris population (10 cm in size or larger) has increased at a nearly constant linear rate of 200 objects per year since the beginning of the space age.
Satellites are required to meet the 25-year rule, which is a limitation in the maximum orbital lifetime for orbiting spacecraft proposed in 2002 by the United Nations Inter Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC). The 25-year rule was slightly revised in 2007 in order to reduce the buildup of orbital debris. Despite this and other numerous debris mitigation policies enacted and followed internationally, space junk is a growing environmental concern in many orbits. The Department of Defense (DoD) Instruction 3100.12, Space Support, requires satellites operating in LEO to de-orbit in less than 25 years at end of life (EOL); similar requirements are imposed by NASA under NSS 1740.14.
Deorbit concepts have been proposed for dealing with the growing problems posed by orbital debris. Most devices use large structures that interact with the atmosphere, magnetic field, or solar environment to deorbit large objects more rapidly than natural decay. Some devices may be better than others relative to the likelihood of collisions during their use.
-
Forum
-
-
-
DISCLAIMER: DO NOT SUBMIT PROPOSALS. This is just a preview. Actual start of the competition depends on the obtainment of funds from donors and investors to cover the costs of the CubeSat bus and the GOLD deorbit system. If these funds are not secured, this program will not proceed.
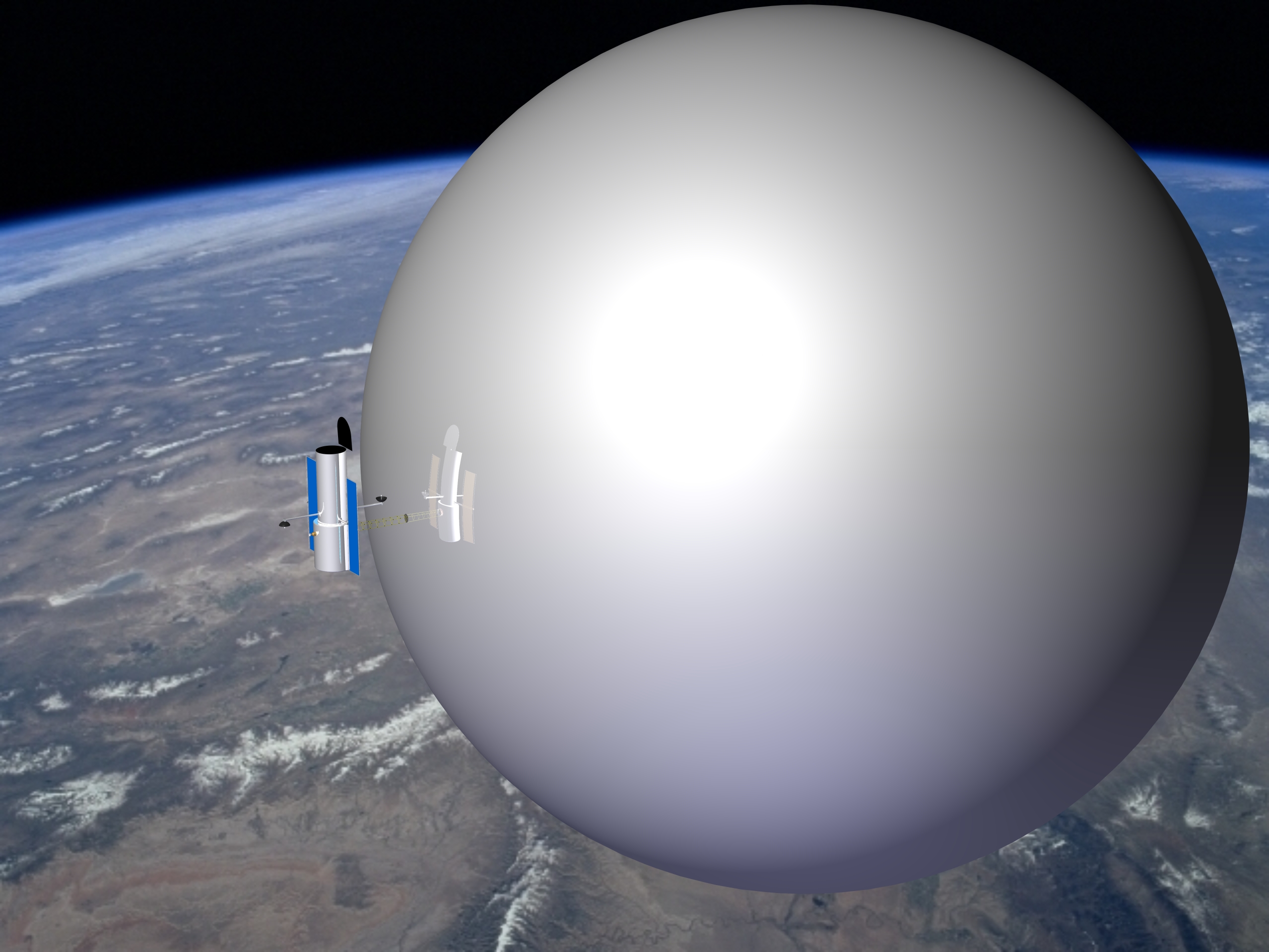
The Enterprise in Space Orbital Debris Mitigation Student Competition is expected to launch to space student experiments that will support a new technology for orbital debris mitigation or develop new experiments for orbital debris detection. When this competition starts (date TBD), it will be led by Global Aerospace Corporation (GAC), the organization in charge of the Enterprise in Space Orbital Debris Mitigation Center for Excellence. The competition will be organized in different phases, at the end of which the best experiments will fly to space. GAC will manage the competition, supervise the students, and select the best experiments that will move on to the next phases. The experiments will support the Gossamer Orbit Lowering Device (GOLD) inflatable deorbit system or will perform orbital debris detection.
-
-
This Cybrary is a repository that contains a wealth of information associated with Orbital Space Debris Mitigation, including research papers, topical information, and links.
Papers can be submitted to the Cybrary and, once they are approved by the Cybrary manager, they will be posted.
-
URL
Internet sites for research.
-
-
-
The Global Aerospace Corporation (GAC) website provides resource material related to the Gossamer Orbit Lowering Device (GOLD) and more in general, orbital debris mitigation. The resources include press releases, news articles, videos, and conference and journal papers.
-
Journal
-
-
-
URL
Instructions:
A. Click the link above. A pop-up window opens.
B. Double click in an empty spot on the board. A small window opens to add your idea.
- Click Title and enter a title.
- Click the text and enter new text.
- Click the image to upload or include document or URL. Click outside the box to save.
- Click your new post and drag or move to a different spot on the board.
C. Close the pop-up window and re-open it to view what you are sharing.
- Click Title and enter a title.
-
